
Info
Note: This is my personal blog, all contents here is not for commercial, they were collected from many sources which will put in Ref section
What is Karpenter ?
Karpenter is a node-based scaling solution created for Kubernetes and aims to improve efficiency costs and . It's a great solution because we don't have to configure instance types or create node pools , which drastically simplifies configuration. On the other hand, integration with Spot instances is painless and allows us to reduce our costs (up to 90% less than On-Demand instances)
Reasons to use Karpenter
Before the launch of Karpenter, Kubernetes users relied primarily on Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling groups and the Kubernetes Cluster Autoscaler (CAS) to dynamically adjust the compute capacity of their clusters. With Karpenter, you don’t need to create dozens of node groups to achieve the flexibility and diversity you get with Karpenter. Moreover, Karpenter is not as tightly coupled to Kubernetes versions (as CAS is) and doesn’t require you to jump between AWS and Kubernetes APIs.
Karpenter consolidates instance orchestration responsibilities within a single system, which is simpler, more stable and cluster-aware. Karpenter was designed to overcome some of the challenges presented by Cluster Autoscaler by providing simplified ways to:
- Provision nodes based on workload requirements
- Create diverse node configurations by instance type, using flexible workload provisioner options. Instead of managing many specific custom node groups, Karpenter could let you manage diverse workload capacity with a single, flexible provisioner.
- Achieve improved pod scheduling at scale by quickly launching nodes and scheduling pods.
What need for an auto-scaling-node kubernetes cluster?
- AWS CLI
- eksctl
- kubectl
- helm
Configure the AWS CLI with a user that has sufficient privileges to create an EKS cluster , IAM Roles . Verify that the CLI can authenticate properly by running aws sts get-caller-identity .
Karpenter Architecture?
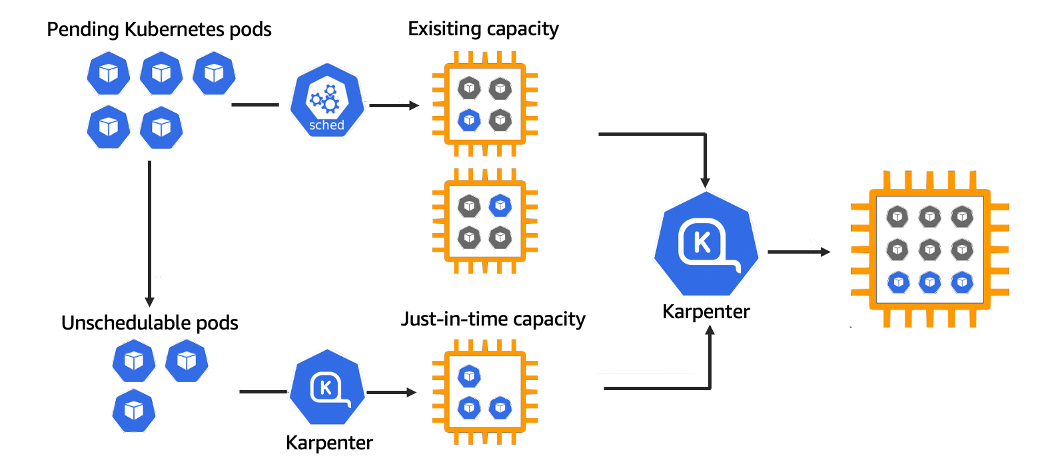
Karpenter works with the Kubernetes scheduler observing incoming pods throughout the lifetime of the cluster. It starts or stops nodes to optimize application availability and cluster utilization. When there is enough capacity in the cluster, the Kubernetes scheduler will place the incoming pods as usual.
When pods are started that cannot be scheduled using existing cluster capacity, Karpenter bypasses the Kubernetes scheduler and works directly with your provider's compute service to start the minimum compute resources needed in those pods and associate pods with provisioning nodes.
When pods are removed , Karpenter looks for opportunities to terminate underutilized nodes.
Set environment variables
After setting up the tools, set the Karpenter version number:
export KARPENTER_VERSION=v0.26.1Then set the following environment variable:
echo $KARPENTER_VERSION $CLUSTER_NAME $AWS_DEFAULT_REGION $AWS_ACCOUNT_ID $TEMPOUTCreate resources
Create a basic cluster with eksctl . The following cluster configuration will:
- Use CloudFormation to set up the infrastructure needed by the EKS cluster.
- Create a Kubernetes service account and AWS IAM Role, and associate them using IRSA to let Karpenter launch instances.
- Add the Karpenter node role to the aws-auth configmap to allow nodes to connect.
- Use AWS EKS managed node groups for the kube-system and karpenter namespaces. Uncomment fargateProfiles settings (and comment out managedNodeGroups settings) to use Fargate for both namespaces instead.
- Set KARPENTER_IAM_ROLE_ARN variables.
- Create a role to allow spot instances.
- Run helm to install karpenter
Get the CloudFormation pre-deploy code
curl -fsSL https://karpenter.sh/"${KARPENTER_VERSION}"/getting-started/getting-started-with-eksctl/cloudformation.yaml > $TEMPOUT && cat $TEMPOUT
Then you will have these config, if you need to modify, please feel free to do so
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: "2010-09-09"
Description: Resources used by https://github.com/aws/karpenter
Parameters:
ClusterName:
Type: String
Description: "EKS cluster name"
Resources:
KarpenterNodeInstanceProfile:
Type: "AWS::IAM::InstanceProfile"
Properties:
InstanceProfileName: !Sub "KarpenterNodeInstanceProfile-${ClusterName}"
Path: "/"
Roles:
- Ref: "KarpenterNodeRole"
KarpenterNodeRole:
Type: "AWS::IAM::Role"
Properties:
RoleName: !Sub "KarpenterNodeRole-${ClusterName}"
Path: /
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: "2012-10-17"
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Principal:
Service:
!Sub "ec2.${AWS::URLSuffix}"
Action:
- "sts:AssumeRole"
ManagedPolicyArns:
- !Sub "arn:${AWS::Partition}:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEKS_CNI_Policy"
- !Sub "arn:${AWS::Partition}:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEKSWorkerNodePolicy"
- !Sub "arn:${AWS::Partition}:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEC2ContainerRegistryReadOnly"
- !Sub "arn:${AWS::Partition}:iam::aws:policy/AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore"
KarpenterControllerPolicy:
Type: AWS::IAM::ManagedPolicy
Properties:
ManagedPolicyName: !Sub "KarpenterControllerPolicy-${ClusterName}"
PolicyDocument:
Version: "2012-10-17"
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Resource: "*"
Action:
# Write Operations
- ec2:CreateFleet
- ec2:CreateLaunchTemplate
- ec2:CreateTags
- ec2:DeleteLaunchTemplate
- ec2:RunInstances
- ec2:TerminateInstances
# Read Operations
- ec2:DescribeAvailabilityZones
- ec2:DescribeImages
- ec2:DescribeInstances
- ec2:DescribeInstanceTypeOfferings
- ec2:DescribeInstanceTypes
- ec2:DescribeLaunchTemplates
- ec2:DescribeSecurityGroups
- ec2:DescribeSpotPriceHistory
- ec2:DescribeSubnets
- pricing:GetProducts
- ssm:GetParameter
- Effect: Allow
Action:
# Write Operations
- sqs:DeleteMessage
# Read Operations
- sqs:GetQueueAttributes
- sqs:GetQueueUrl
- sqs:ReceiveMessage
Resource: !GetAtt KarpenterInterruptionQueue.Arn
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- iam:PassRole
Resource: !Sub "arn:${AWS::Partition}:iam::${AWS::AccountId}:role/KarpenterNodeRole-${ClusterName}"
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- eks:DescribeCluster
Resource: !Sub "arn:${AWS::Partition}:eks:${AWS::Region}:${AWS::AccountId}:cluster/${ClusterName}"
KarpenterInterruptionQueue:
Type: AWS::SQS::Queue
Properties:
QueueName: !Sub "${ClusterName}"
MessageRetentionPeriod: 300
KarpenterInterruptionQueuePolicy:
Type: AWS::SQS::QueuePolicy
Properties:
Queues:
- !Ref KarpenterInterruptionQueue
PolicyDocument:
Id: EC2InterruptionPolicy
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Principal:
Service:
- events.amazonaws.com
- sqs.amazonaws.com
Action: sqs:SendMessage
Resource: !GetAtt KarpenterInterruptionQueue.Arn
ScheduledChangeRule:
Type: 'AWS::Events::Rule'
Properties:
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.health
detail-type:
- AWS Health Event
Targets:
- Id: KarpenterInterruptionQueueTarget
Arn: !GetAtt KarpenterInterruptionQueue.Arn
SpotInterruptionRule:
Type: 'AWS::Events::Rule'
Properties:
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.ec2
detail-type:
- EC2 Spot Instance Interruption Warning
Targets:
- Id: KarpenterInterruptionQueueTarget
Arn: !GetAtt KarpenterInterruptionQueue.Arn
RebalanceRule:
Type: 'AWS::Events::Rule'
Properties:
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.ec2
detail-type:
- EC2 Instance Rebalance Recommendation
Targets:
- Id: KarpenterInterruptionQueueTarget
Arn: !GetAtt KarpenterInterruptionQueue.Arn
InstanceStateChangeRule:
Type: 'AWS::Events::Rule'
Properties:
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.ec2
detail-type:
- EC2 Instance State-change Notification
Targets:
- Id: KarpenterInterruptionQueueTarget
Arn: !GetAtt KarpenterInterruptionQueue.Arn
Apply the CloudFormation with this command
aws cloudformation deploy \
--stack-name "Karpenter-${CLUSTER_NAME}" \
--template-file "${TEMPOUT}" \
--capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM \
--parameter-overrides "ClusterName=${CLUSTER_NAME}"

Create a eks cluster with these config below
eksctl create cluster -f - << EOF
---
apiVersion: eksctl.io/v1alpha5
kind: ClusterConfig
metadata:
name: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
region: ${AWS_DEFAULT_REGION}
version: "1.24"
tags:
karpenter.sh/discovery: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
iam:
withOIDC: true
serviceAccounts:
- metadata:
name: karpenter
namespace: karpenter
roleName: ${CLUSTER_NAME}-karpenter
attachPolicyARNs:
- arn:aws:iam::${AWS_ACCOUNT_ID}:policy/KarpenterControllerPolicy-${CLUSTER_NAME}
roleOnly: true
iamIdentityMappings:
- arn: "arn:aws:iam::${AWS_ACCOUNT_ID}:role/KarpenterNodeRole-${CLUSTER_NAME}"
username: system:node:{{EC2PrivateDNSName}}
groups:
- system:bootstrappers
- system:nodes
managedNodeGroups:
- instanceType: m5.large
amiFamily: AmazonLinux2
name: ${CLUSTER_NAME}-ng
desiredCapacity: 2
minSize: 1
maxSize: 10
## Optionally run on fargate
# fargateProfiles:
# - name: karpenter
# selectors:
# - namespace: karpenter
EOF
export CLUSTER_ENDPOINT="$(aws eks describe-cluster --name ${CLUSTER_NAME} --query "cluster.endpoint" --output text)"
export KARPENTER_IAM_ROLE_ARN="arn:aws:iam::${AWS_ACCOUNT_ID}:role/${CLUSTER_NAME}-karpenter"
echo $CLUSTER_ENDPOINT $KARPENTER_IAM_ROLE_ARN
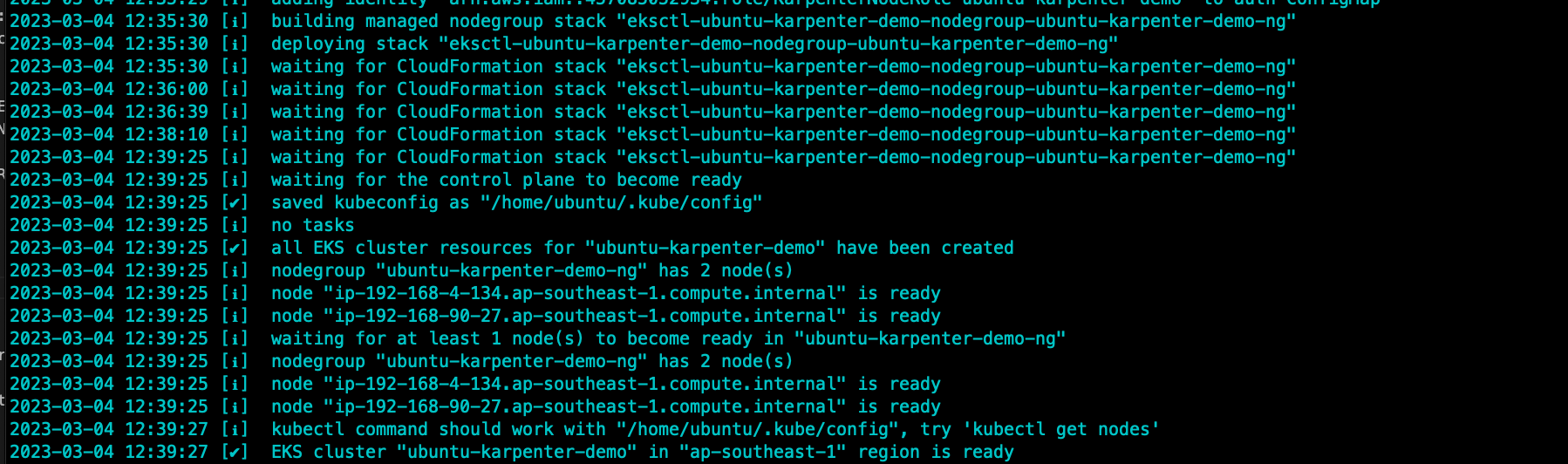
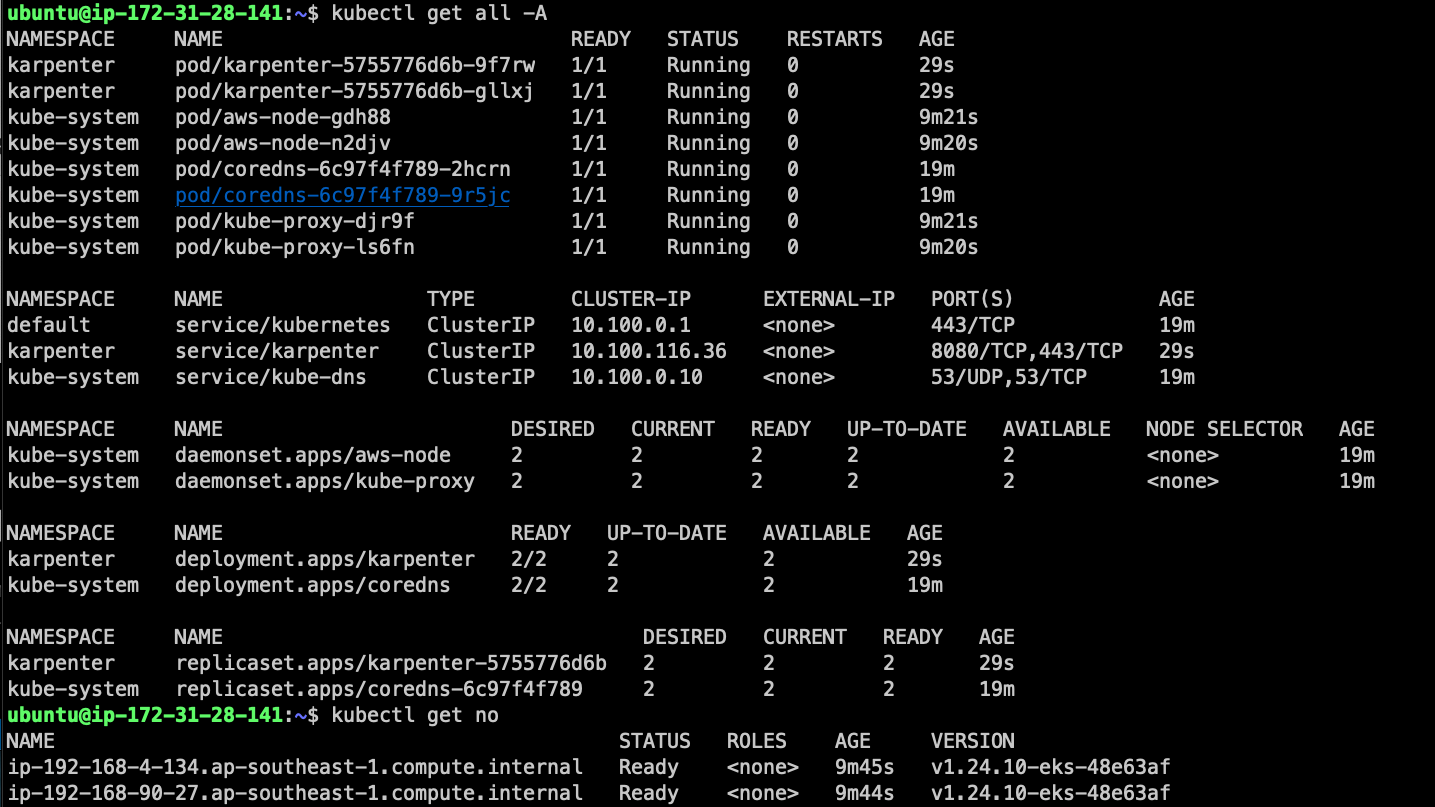
Verify if it ok
aws iam create-service-linked-role --aws-service-name spot.amazonaws.com || true
# If the role has already been successfully created, you will see:
# An error occurred (InvalidInput) when calling the CreateServiceLinkedRole operation: Service role name AWSServiceRoleForEC2Spot has been taken in this account, please try a different suffix.
helm upgrade --install karpenter oci://public.ecr.aws/karpenter/karpenter --version ${KARPENTER_VERSION} --namespace karpenter --create-namespace \
--set serviceAccount.annotations."eks\.amazonaws\.com/role-arn"=${KARPENTER_IAM_ROLE_ARN} \
--set settings.aws.clusterName=${CLUSTER_NAME} \
--set settings.aws.defaultInstanceProfile=KarpenterNodeInstanceProfile-${CLUSTER_NAME} \
--set settings.aws.interruptionQueueName=${CLUSTER_NAME} \
--wait
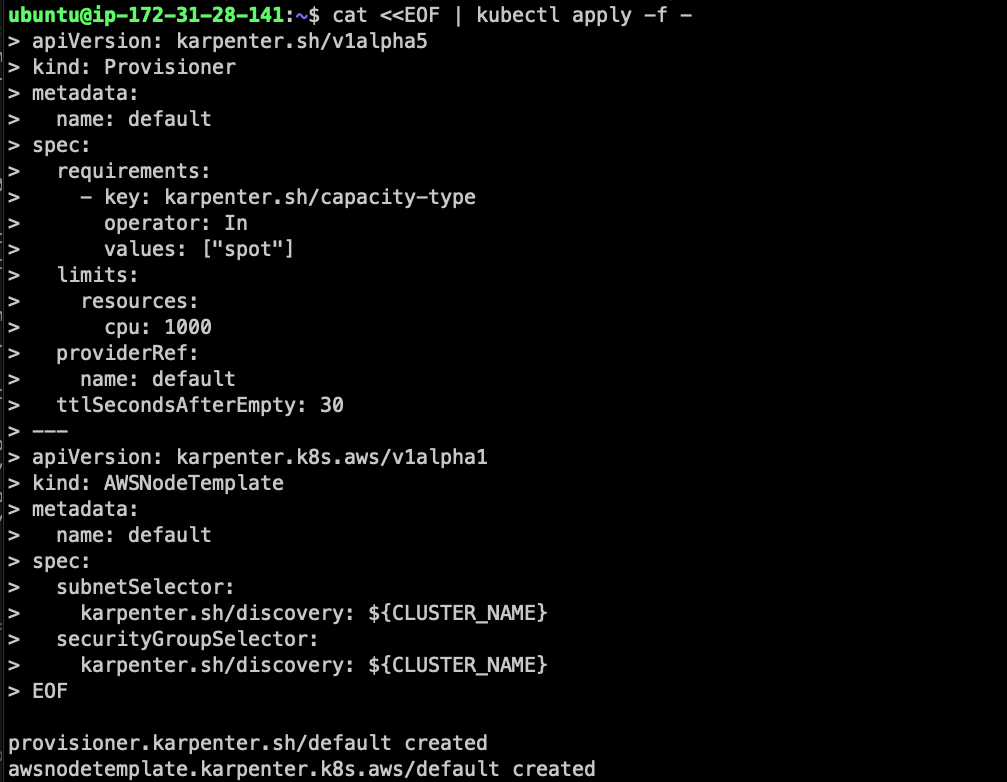
Create a CRD Karpenter with Provisioner and Node Template
nano karpenter-crd.yaml
apiVersion: karpenter.sh/v1alpha5
kind: Provisioner
metadata:
name: default
spec:
requirements:
- key: karpenter.sh/capacity-type
operator: In
values: ["spot"]
limits:
resources:
cpu: 1000
providerRef:
name: default
ttlSecondsAfterEmpty: 30
---
apiVersion: karpenter.k8s.aws/v1alpha1
kind: AWSNodeTemplate
metadata:
name: default
spec:
subnetSelector:
karpenter.sh/discovery: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
securityGroupSelector:
karpenter.sh/discovery: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
You can define more requirements like instance-type or architect by using this link, by defautl, if no instance type constraints are defined, Karpenter will set default instance type constraints on your Provisioner that supports most common user workloads:
requirements:
- key: karpenter.k8s.aws/instance-category
operator: In
values: ["c", "m", "r"]
- key: karpenter.k8s.aws/instance-generation
operator: Gt
values: ["2"]
kubectl apply -f karpenter-crd.yaml
Testing
At the time we provision the eks, only 2 nodes as worker role

We will try to create a deployment with pause image from kubernetes with replica=0, then scale up to 5 and see the no-of-node increase automatically
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: inflate
spec:
replicas: 0
selector:
matchLabels:
app: inflate
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: inflate
spec:
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0
containers:
- name: inflate
image: public.ecr.aws/eks-distro/kubernetes/pause:3.7
resources:
requests:
cpu: 1
EOF
then try to scale the deployment to 5 replicas
kubectl scale deployment inflate --replicas 5
kubectl logs -f -n karpenter -l app.kubernetes.io/name=karpenter -c controller
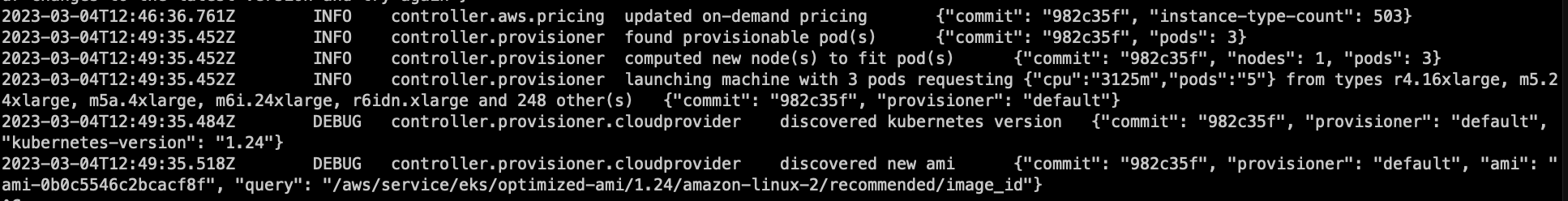
Try to scale-down to see if nodes wwould be down too
kubectl scale deployment inflate --replicas 0
kubectl logs -f -n karpenter -l app.kubernetes.io/name=karpenter -c controller
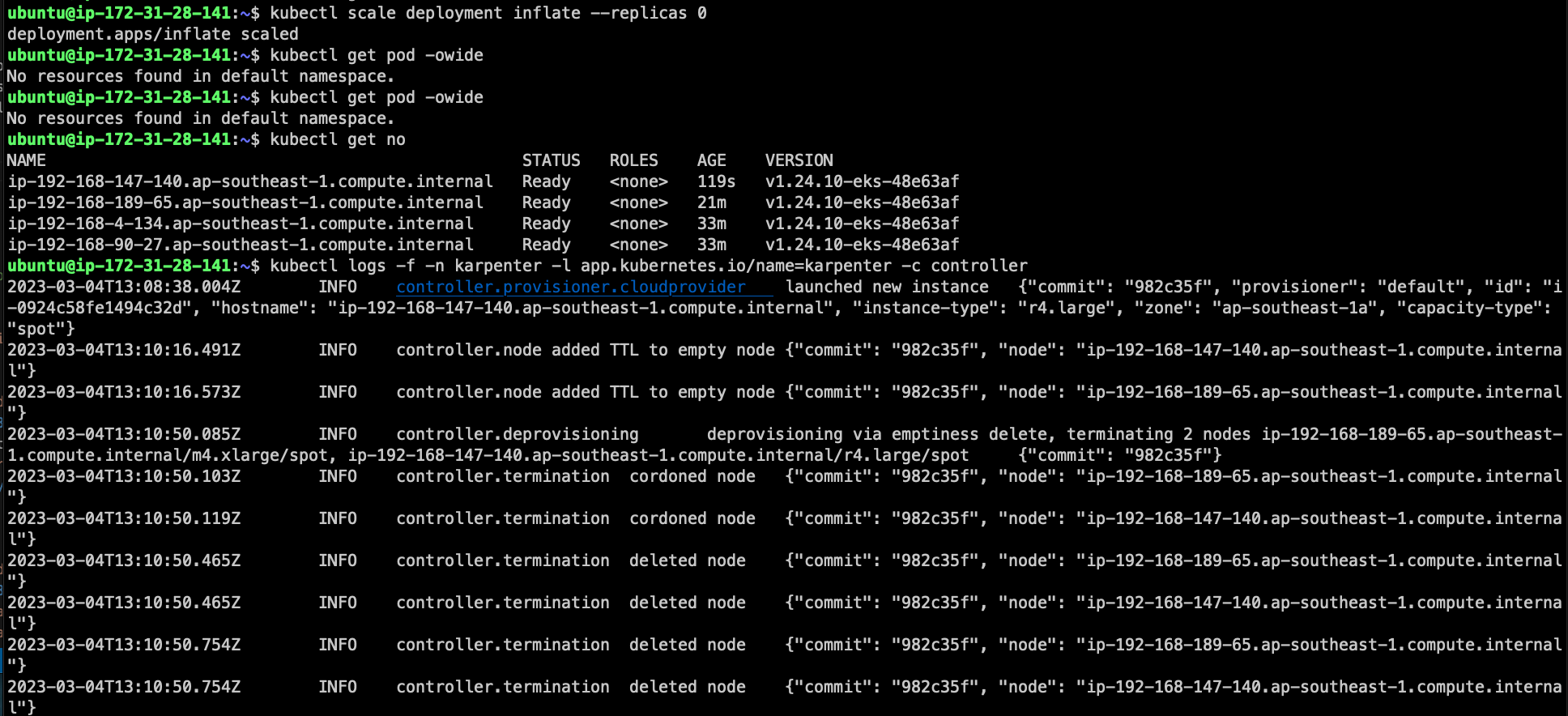
Reference:
 Thi
Thi